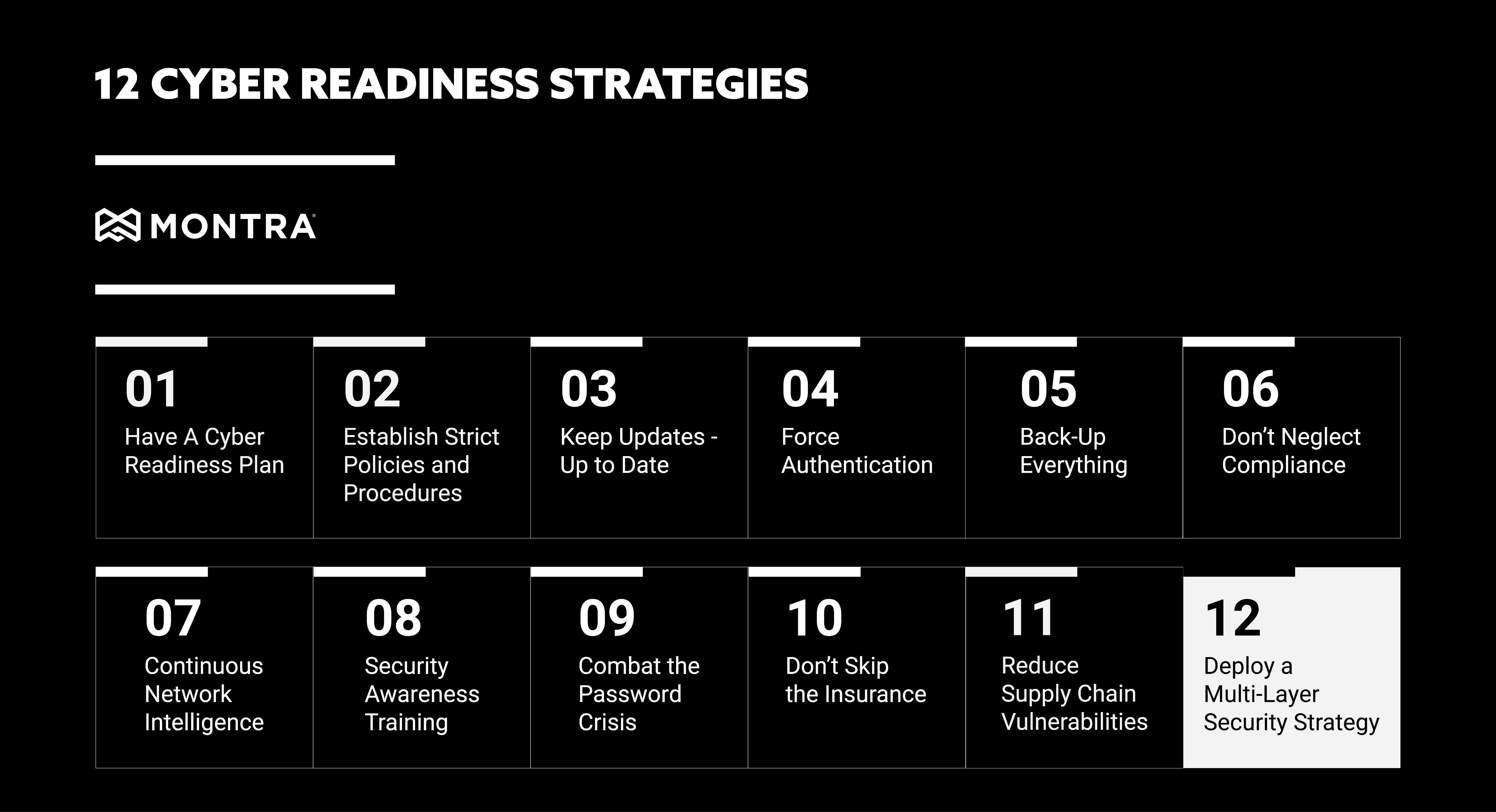
Remote Management System Deployment: Beware of the Security Risks
Remote management systems have evolved into a valuable tool for IT professionals, enabling remote access, monitoring, and management of their organization’s IT infrastructure. However, as with any technology, they come with inherent risks. Deploying remote management systems without considering the potential security issues can lead to disaster, ultimately undermining the benefits of remote access. In this blog post, we will explore security considerations that every CIO, CISO, and IT Director must keep in mind when deploying remote management systems.
Comprehensive Security Policy
Before starting the deployment process of remote management systems, it is important to have a comprehensive security policy in place. A comprehensive security policy should include the security measures that will be implemented to safeguard your organization’s assets. The policy should also define the roles and responsibilities of each member of the IT team, and specify the security controls in addition to the access controls that will be in place. By having a detailed security policy, you will make sure that the remote management system is deployed in a secure manner.
According to the Verizon 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report, over 70% of breaches were perpetrated by outsiders, and a significant 45% of those breaches featured hacking. Among those incidents, 37% exploited vulnerabilities in virtual private network (VPN) services, which are a common component of remote management systems. Moreover, a study by Ponemon Institute found that the average cost of a data breach in 2020 was a heart-stopping $3.86 million. So, when we’re discussing comprehensive security policies, we’re not just setting the rules for a game – we’re talking about a potential multi-million-dollar rescue operation.
Secure Communication Channels
Remote management systems operate using a network connection. Therefore, it is essential to use a secure communication channel to prevent unauthorized access. Encryption is the standard method for encoding messages so that only authorized parties can read them. Encryption can also protect against man-in-the-middle attacks by securing communication channels with secure protocols like SSL, TLS, and SSH. So, let’s make no bones about it, failing to encrypt your communications is like leaving your front door wide open with a giant neon sign that reads “Free Stuff Here – No Need to Knock”.
Encryption isn’t enough though. According to data from the 2021 Cybersecurity Report by Check Point Software, encrypted attacks, where threat actors hide their exploits in encrypted traffic, have seen a stark rise of almost 50% in the second half of 2020. The report also reveals that SSL/TLS encrypted attacks accounted for 23% of all attacks in 2020. Furthermore, the 2020 Trustwave Global Security Report indicates that a massive 20% of cyber attacks targeted Secure Shell (SSH) protocols. IT organizations need to be smart about how they handle encrypted traffic, especially in remote locations with less sophisticated network firewalls.
Access Control and Authorization
Access control is a fundamental aspect of any security policy. The access control policy for remote management systems should be based on the principle of granting the least privileges. According to the Microsoft Security Intelligence Report, in 2020, over 70% of breaches involved privilege misuse. Furthermore, a survey by Centrify revealed that 74% of respondents whose organizations had been breached acknowledged it involved access to a privileged account—these are the keys that unlock access to systems and sensitive data. Granting the least privileges means that users are given only the permissions they need to perform their duties, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Authorization-based access control mechanisms can be used to further ensure that users have access to the resources that they need.
Implementing least privilege access can reduce the attack surface, improve audit and compliance visibility, and reduce the risk of insider threats. Clearly, unfettered access is about as advisable as leaving your car keys in the ignition of your unlocked car at a kleptomaniacs’ convention.
Authentication Mechanisms
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user attempting to access a particular resource. Authentication mechanisms should be implemented to identify and verify users before granting access. The authentication mechanism should not only verify a user’s identity but also confirm that the user has permission to perform the required tasks. Multifactor authentication should also be used, requiring a password and another form of authentication, such as fingerprint recognition or a smart card.
The 2020 State of Password and Authentication Security Behaviors Report by Ponemon Institute found that 51% of respondents reuse passwords across business and personal accounts, making multi-factor authentication even more critical. In the same vein, Google reported that accounts protected by multi-factor authentication block 99.9% of automated attacks. Further supporting these findings, Symantec’s Internet Security Threat Report stated that 80% of breaches could have been prevented by two-factor authentication. So, if you’re choosing to ignore multi-factor authentication, you are opening the door to unauthorized access to your systems and data.
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Continuous monitoring and auditing help to identify and mitigate risks. It is essential to have tools in place that can detect suspicious activities and take remedial actions when necessary. Remote management systems should have auditing built into them, allowing security personnel to carefully track the activities that occur on the network and monitor the logs to identify any unusual activity.
According to the 2020 Cost of a Data Breach Report by IBM, companies that identified a breach in less than 200 days spent $1 million less on the total cost of the breach – a pretty penny saved by acting swiftly. Additionally, the SANS Institute revealed that continuous monitoring reduces the average time to identify a threat to 14.5 hours, a drastic improvement from the industry average of 206 days. Further strengthening this stance, a report by the Ponemon Institute indicates that organizations without security automation experienced breaches that were 95% more costly than breaches at organizations with extensive security automation. So, if you think continuous monitoring and auditing are like watching paint dry, remember – it’s considerably more exciting than watching your company’s finances drain away post-data breach.
Deploying remote management systems can be a powerful tool for IT professionals, enabling remote access, monitoring, and management of their organization’s IT infrastructure. However, security considerations must be taken into account during deployment and regular operations. We have highlighted the most crucial security considerations such as comprehensive security policy, secure communication channels, access control and authorization, authentication mechanisms, and continuous monitoring and auditing. Therefore, IT professionals must ensure they have a robust and comprehensive security policy in place before deploying remote management systems to protect their organization’s assets from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Sources
Trustwave Global Security Report. Trustwave Holdings, Inc. 2020. Link to report
Microsoft Security Intelligence Report. Microsoft Corporation. 2020. Link to report
Centrify Privileged Access Management in the Modern Threatscape. Centrify Corporation. 2020. Link to survey
The 2020 State of Password and Authentication Security Behaviors Report. Ponemon Institute. 2020. Link to report
Symantec Internet Security Threat Report. Symantec Corporation. 2020. Link to report
Cost of a Data Breach Report. IBM Corporation. 2020. Link to report
SANS Institute Report: Reducing Attack Surface with Security Control Automation. SANS Institute. 2020. Link to report
Ponemon Institute: The Cost of Inaction for Cybersecurity. Ponemon Institute. 2020. Link to report