The Evolution of IT Asset Management Software in 2024: Converge the Data
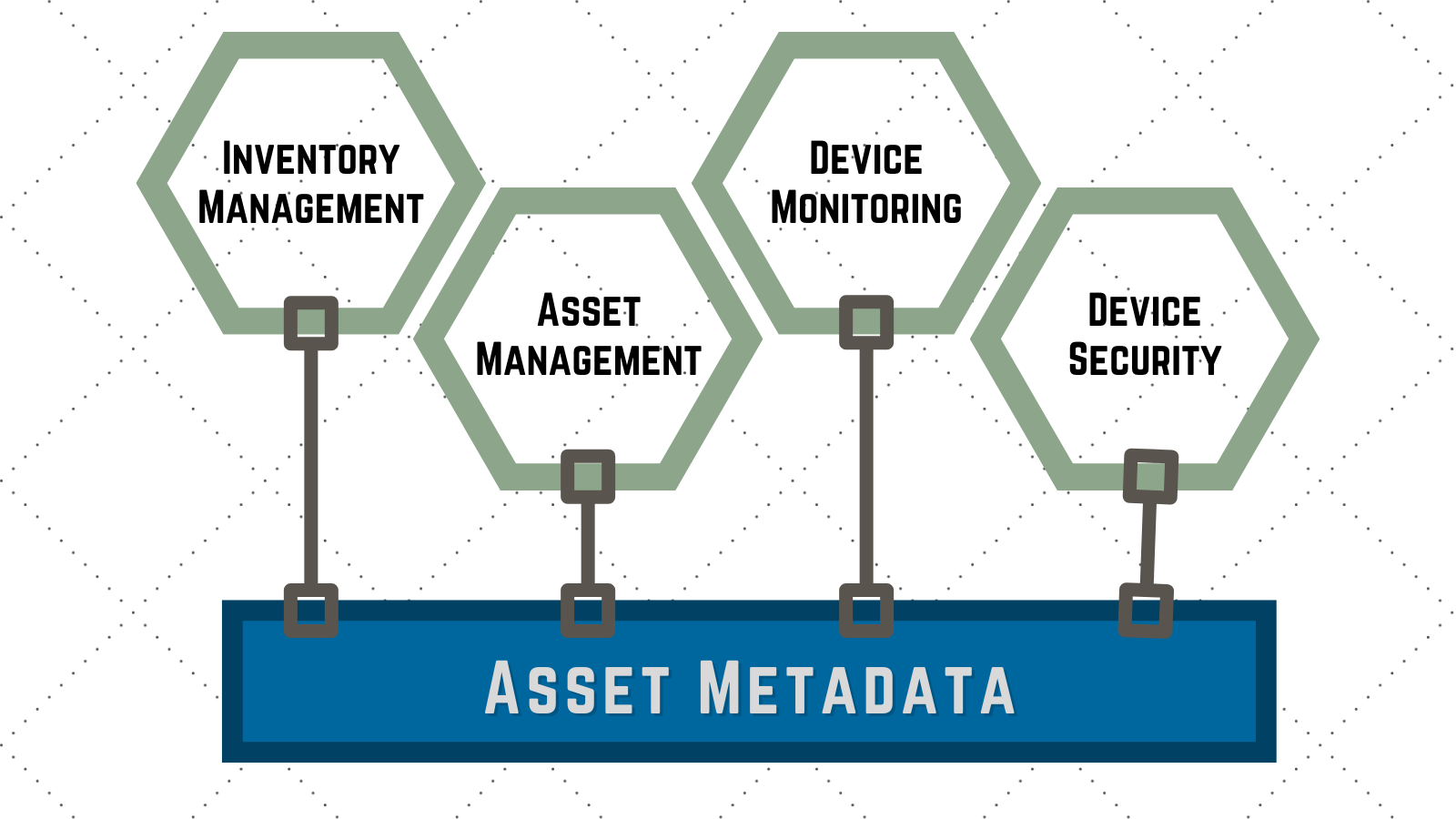
As IT asset management continues to evolve, it increasingly intersects with adjacent domains such as device monitoring, device security, and inventory management. We examine here the latest trends shaping asset management software in 2024, examining notable advancements, emerging features, and evolving end-to-end processes. Additionally, we explore current challenges in asset management solutions and industry strategies addressing these issues.
Latest Trends
Integration with Device Monitoring and Security
One of the most significant trends in asset management is the integration with device monitoring and security. The rise of IoT technologies has enabled real-time monitoring of assets, providing invaluable insights into asset performance and maintenance needs^1. This integration ensures that organizations can not only track their assets but also monitor their condition, leading to proactive maintenance and reduced downtime.
For instance, consider a manufacturing company that employs an extensive array of machinery and equipment. By integrating IoT-enabled sensors on these machines, the company can receive real-time data on various parameters such as temperature, vibration, and operational status. If a particular machine begins to overheat, the system immediately sends an alert, enabling the maintenance team to intervene before a critical failure occurs. This proactive approach not only enhances the longevity of the assets but also significantly reduces unexpected downtime, ensuring continuous and efficient production. Furthermore, incorporating advanced security protocols in these IoT systems safeguards against cyber threats, protecting both the data and the operational integrity of the assets.
Enhanced Inventory Management Features
Inventory management has typically focused on racking assets prior to deployment or when assets have been returned to storage. The data in these systems heavily overlaps with the data in asset management and device monitoring systems. To provide a more seamless integrated view of data about IT assets, modern asset management software should incorporate inventory management. This includes warehousing information as well as tracking the processes serving it including shipping & receiving, pick-pack, kitting, and pre-deployment configuration and imaging^2. Such features streamline the management of physical IT assets, ensuring optimal utilization and compliance. For digital assets it helps ensure licenses are being deployed properly and the unused licenses are managed more closely to reduce cost.
Evolution of IT Asset Management (ITAM) Solutions
The landscape of IT asset management software is constantly evolving, with providers offering more sophisticated tools that cover the entire lifecycle of an asset—from procurement to disposal^3. In 2024, there is a marked shift towards solutions that provide comprehensive visibility and control over IT infrastructure, supporting a holistic approach to asset management.
Advancements in Asset Management Software
Full Lifecycle Asset Management
Full lifecycle asset management involves managing every stage of an asset’s lifecycle, including procurement, configuration, deployment, monitoring, and returns^4. Modern software solutions are optimized to support each of these stages seamlessly, offering features like automated procurement processes, real-time configuration updates, continuous monitoring, and efficient return management. This comprehensive approach ensures that organizations can manage their assets efficiently, reducing costs and improving overall productivity.
Automation and Artificial Intelligence
Automation and AI are driving significant improvements in asset management software. Advanced algorithms can predict maintenance needs, automate routine tasks, and provide actionable insights based on data analysis. This leads to more efficient asset utilization and extends the lifespan of assets through timely maintenance^5.
Cloud-Based Solutions and Mobility
Cloud-based asset management solutions are becoming the norm, offering scalability, flexibility, and remote accessibility. These solutions enable organizations to manage their assets from anywhere, using any device, which is particularly beneficial for businesses with distributed operations^6.
Challenges in Asset Management Solutions
Complexity and Integration Issues
One of the primary challenges with asset management solutions today is their complexity and the difficulty of integrating them with existing systems. Many organizations struggle with disparate systems that do not communicate effectively, leading to inefficiencies and data silos^7. To address this, the industry is focusing on developing more interoperable solutions that can seamlessly integrate with other enterprise systems.
Data Security Concerns
As asset management systems become more integrated with IoT and other technologies, data security becomes a critical concern. Protecting sensitive asset information from cyber threats is paramount. Providers are enhancing security features, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure access controls, to safeguard data^8.
Cost and Resource Constraints
Implementing and maintaining advanced asset management software can be costly, and many organizations face resource constraints. To mitigate this, software providers are offering scalable solutions with flexible pricing models, allowing businesses to start small and expand as needed^9.
Conclusion
The evolution of asset management software in 2024 is marked by its convergence with device monitoring, security, and inventory management. With advancements in AI, automation, and cloud technology, end-to-end asset management is becoming a vital component of IT infrastructure management. Despite the challenges of complexity, integration, and cost, the industry is making strides in developing more efficient, secure, and accessible solutions.
By leveraging these modern asset management tools, organizations can achieve better asset utilization, enhanced security, and improved operational efficiency, positioning themselves for success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Footnotes
- https://www.digi.com/blog/post/iot-in-asset-management ↩
- https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/inventory-management/inventory-management-asset-management.shtml ↩
- https://blog.invgate.com/best-practices-it-asset-discovery-and-inventory-management ↩
- https://www.assetinfinity.com/blog/the-evolution-of-asset-management-software-whats-new-in-2024-with-asset-infinity ↩
- https://www.pwc.com/us/en/industries/financial-services/library/asset-wealth-management-trends.html ↩
- https://limblecmms.com/blog/asset-inventory-management/ ↩
- https://infraon.io/blog/asset-management-trends-2023/ ↩
- https://www.assetinfinity.com/blog/asset-management-trends-in-2023 ↩
- https://blog.invgate.com/best-it-asset-management-and-inventory-tools ↩